How to Calculate Flow Rate Through a Valve
 Calculating flow rate is an important step in selecting the correct valve for your application. Selecting a valve that cannot handle the proper flow needed in the application can cause inefficiencies and even damage equipment. On the other hand, selecting a valve that can easily handle the flow requirements may result in higher equipment costs then are necessary, and extra weight. This is because as flow rate requirements increase, so does the size and therefore weight of the valve.
Calculating flow rate is an important step in selecting the correct valve for your application. Selecting a valve that cannot handle the proper flow needed in the application can cause inefficiencies and even damage equipment. On the other hand, selecting a valve that can easily handle the flow requirements may result in higher equipment costs then are necessary, and extra weight. This is because as flow rate requirements increase, so does the size and therefore weight of the valve.
Each valve will have a Cv rating, which represents the quantity of room temperature water that will flow (in GPM) through the valve with a 1 PSI pressure differential. Cv is directly rated to flow rate, so the higher the Cv, the more flow that can travel through the valve. Cv can be calculated based on the below equations, one for liquid, and one for gases.
Liquid Flow:

Gas Flow: Assuming Inlet Pressure (P1) is greater than Outlet Pressure (P2)
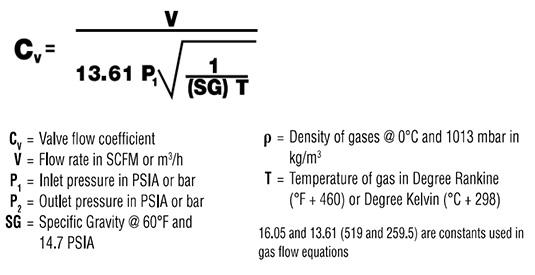
=Cv.*(dP./SG.)^1/2
=0.02*(100/1)^1/2
=0.2 GPM
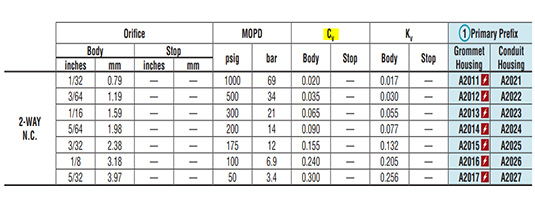
If you despise math equations like these, you’re in luck because we’ve done them for you. For each prefix/orifice size we’ve calculated what the maximum flow rate would be if you were to input the maximum amount of MOPD (Max Operating Pressure Differential). If you input less pressure, then your flow rate will be lower. Please review these flow rate charts based on each valve series.
 SEARCH OUR RESOURCE CENTER
SEARCH OUR RESOURCE CENTER
